Blog
Dental hygiene tips for healthy teeth & gums
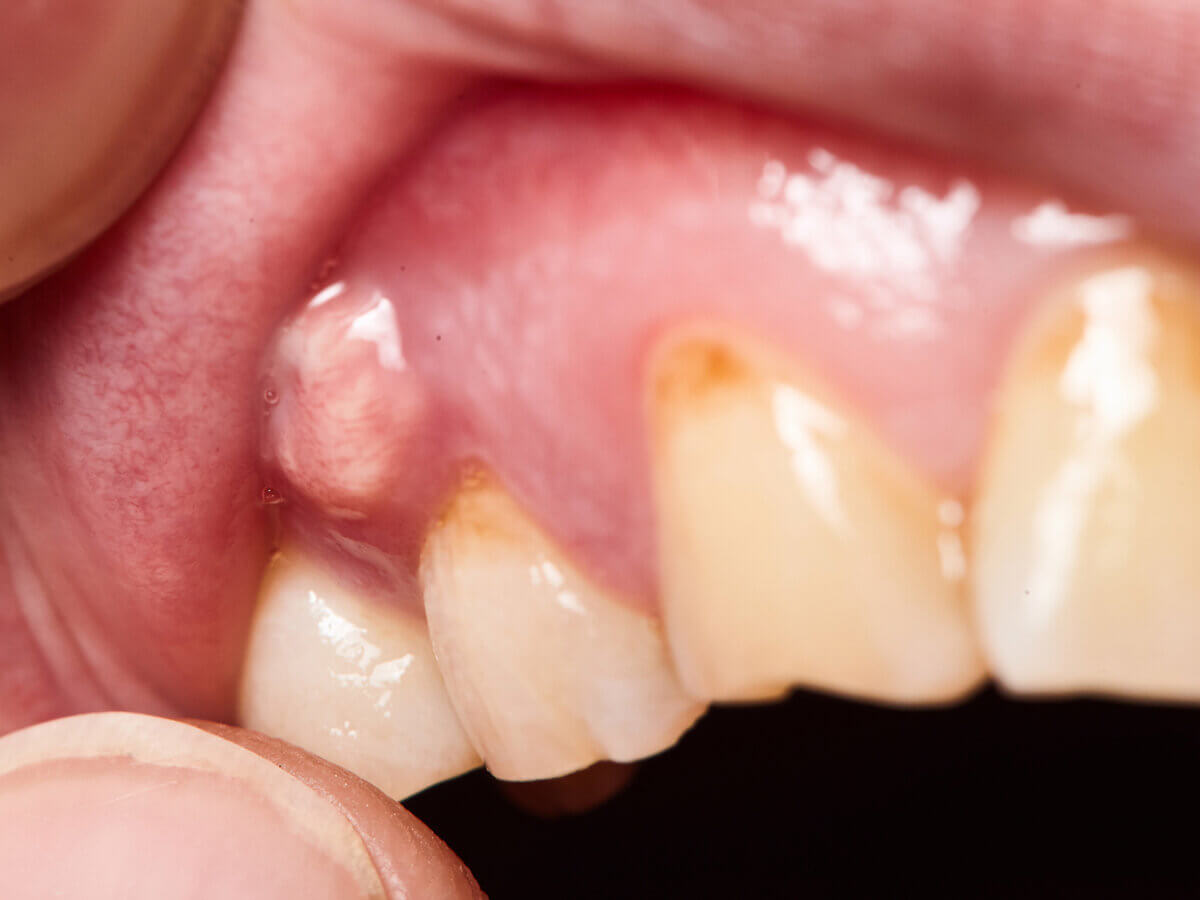
How Does A Tooth Abscess Affect My Oral And Overall Health?
A tooth abscess (also called a dental abscess) is a pocket of pus and bacteria inside the mouth. Dental infection is a common occurrence, but when you develop ulcers in the mouth due to infection, it can be excruciating and dangerous. It is necessary that you know the signs of a dental cyst so that you can seek help and treat them as soon as possible.
A dental abscess is caused due to bacterial infection, and it can form in different areas near your tooth due to different reasons. The blister may be located within your teeth, gums, or even within the bone that supports your teeth. If the cyst is at the tip of your root, it is termed a periapical abscess, and if the blister is inside your gums, it is called a periodontal cyst.
Your dentist can treat the abscess by draining your teeth and getting rid of the infection. This could be followed by a root canal to save your teeth. But if it is a severe case, your doctor might need to pull out your teeth.
To save yourself from all these hassles, you must read on to understand how to figure out if you have a tooth abscess and how it affects your overall health.
Symptoms of Cyst in Dentition
If you have blisters in your pearly whites, you could experience some or all of the following symptoms:
- Constant throbbing pain in teeth, which also spreads to your jawbone, ear, or neck.
- Discomfort or pain with extreme temperatures (too hot or too cold drinks.)
- Discomfort or pain while chewing food or biting down.
- Developing fever.
- The face, neck, or cheek is swollen, which makes it difficult to breathe or swallow food.
- Your mouth smells foul.
- The lymph nodes under your jaw or neck are tender and swollen.
- You suddenly experience a rush of foul-tasting or foul-smelling salty fluid in your mouth.
- Your teeth’ color has changed.
What Kind of Dental Infection Can Cause Abscesses/Cysts?
Cysts in dentition can be caused by three types of tooth infections, as described below:
- Gingival – This is an infection in the gum that usually does not affect your pearly whites or its supporting structures.
- Periapical – If you have a fractured or decayed tooth, it allows bacteria to enter your dentition and spread to the pulp (the innermost part of a tooth that has blood vessels and nerves.) Once bacteria enter the pulp, they can spread the infection to the tip of your dentition’s root and eventually to the surrounding bone and form an abscess.
- Periodontal – This type of infection starts at the bone and tissues that support your pearly whites. This type of abscess is more common in adults and is usually a result of gum disease.
Why Does One Get Tooth Cyst?
Anything that creates an opening in your teeth for bacteria to get inside your teeth or surrounding tissues can lead to blisters in your teeth. Some common causes include:
- Severe cavities – When the enamel (the hard surface of your teeth) is destroyed, it leads to cavities. The bacteria in your mouth break down sugars in your drinks and food, which creates acid that attacks your enamel.
- Injury to teeth – If there is an injury to the face, it can affect the pulp inside your teeth (even when you do not see any visible crack.) This makes your pearly whites prone to infections.
- Cracked, broken, or chipped teeth – Through any opening in your dentition, bacteria can seep inside and spread to the pulp.
- Periodontal or gum disease – When you have gum disease, the tissue around your teeth gets inflamed and infected. With the progress of gum disease, the bacteria gain access to the deeper tissues in your mouth.
How to Diagnose an Abscess in Teeth?
Apart from examining the tissue and your teeth for any signs of infection, your dentist could also recommend a few tests and procedures to understand your issue:
- Dental X-ray – With a dental X-ray, one can know the sources of the dental infection which resulted in the tooth abscess. X-rays will also help your dentist understand if the infection has spread and is affecting other areas in your mouth.
- CT scan – If an X-ray reveals that the infection has spread to other areas, a CT scan will give insight into the extent of the spread of the infection.
- Thermal tests – Thermal tests reveal the health of your pulp.
Does a Tooth Abscess Spread Infection to Other Parts of My Body?
Yes, if the dental infection is not treated, it can affect your overall health, which could even become life-threatening. Untreated dental infection can take weeks to month s to spread to other parts of your body and can lead to the following health issues:
- Heart attack or stroke – Chronic infection is one of the most common causes of cardiovascular issues. Your body responds to infection through inflammation, and when this is in excess, it creates blood clots, and the blood vessels leading to your heart can get overwhelmed. A cyst in your pearly whites increases the risk of heart issues almost three times.
- Sepsis and septic shock – A small infection in dentition could spread all through the body if not treated in time and lead to septic shock. Sepsis causes blood clots and damages blood vessels which compromises your organs. If sepsis progresses to septic shock, your body shuts down with a rapid decrease in blood pressure.
- Cellulitis – A tooth cyst could cause infection of the skin and fat under your skin.
- Pulmonary actinomycosis – This is an infection in your lungs that could result from blisters in your pearly whites.
- Brain abscess – The bacteria in your mouth could result in swelling of a pocket of bacteria in your brain, which could be fatal.
- Cavernous sinus thrombosis – When the blister in your teeth reaches the blood vessels in your sinuses, it could infect them too.
A tooth abscess could wreak havoc on your whole body if not treated in time. The first step towards preventing any oral disease is following an excellent oral regime and regular dental checkups. But if you develop a tooth abscess, then you would need to consult your dentist, who could drain out the infection or perform other procedures, such as a root canal, give antibiotics, etc., to subside the infection and stop it from reaching other parts of your body.
