Blog
Dental hygiene tips for healthy teeth & gums
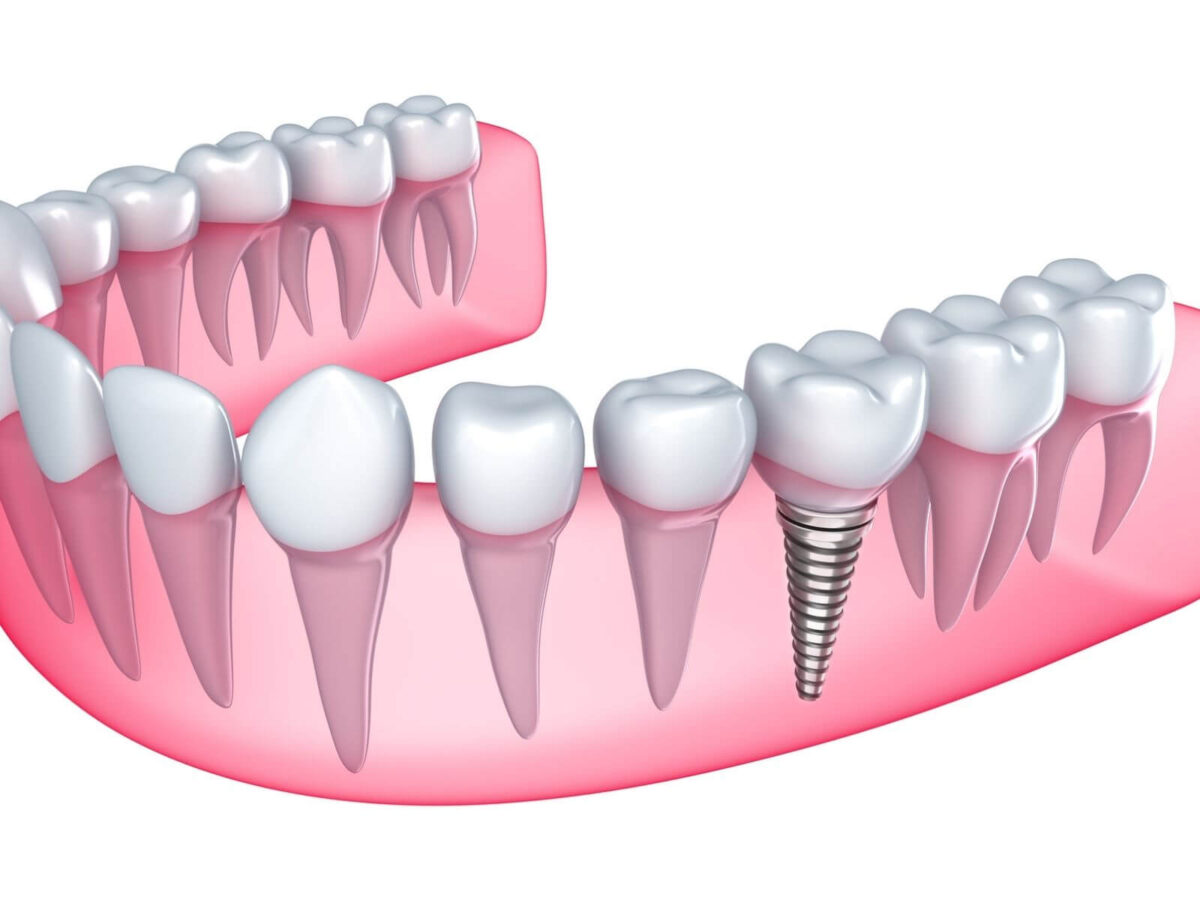
How Can Dental Implants Stop Bone Loss?
Tooth loss restoration achieves its perfect solution through dental implants, which deliver functionality and aesthetic benefits to patients. The degeneration of bone tissue is the primary concern dental implant patients must address.
Patients need to know what treatment options are available to treat bone loss near their dental implants. This article examines why bone tissue diminishes near dental implants, followed by available treatment approaches and preventive techniques to sustain a robust dental smile.
Missing Teeth & Your Jawbone
Bone density, along with structural stability, depends entirely on the nature of external stimuli. When someone bites their teeth, the jawbone gets the needed activation signals. Your teeth initiate numerous intensity points that occur more than hundreds of times daily. When teeth touch during eating, tiny forces between them transfer through the bone until the tissue activates continuous bone healing.
Bone stimulation in the surrounding area ceases after tooth loss, thus causing the surrounding bone to decrease in density. Tooth loss begins a process of weakened bone tissue formation.
The reduction of bone density in the mouth initiates a harmful process of tooth loss, which worsens the destructive cycle.
The constant deterioration of bone tissue from missing many teeth results in facial collapse as this condition shortens the facial area extending from the upper face to the lower chin. Lacking structural support, the lips sag.
People whose teeth are missing present an aged physical appearance due to toothless mouths, which causes them to appear unsmiling. Bone tissue deterioration raises your risk of facial bone breakdown and destroys your capacity to chew or speak properly.
Many bite problems, along with jaw pain, result when moving existing teeth toward gaps.
Signs and Symptoms of Bone Loss Around Dental Implants
Multiple signs will surface to indicate bone loss in the region surrounding a dental implant.
Strong dental implants should respond the same way as natural teeth, but reduced bone triggers unwanted movement.
When bone atrophy occurs, your gums move toward the back, away from the implant.
Part of the body develops pain because dental implants usually do not hurt the tissues.
Too much bone loss lets the gums shift from their normal position to become visible.
Why Is Bone Loss Around Implants a Concern?
Doctors view bone decline around implants as serious because it creates several medical problems.
Strong bone support is needed for the implant because bone provides its main hold. People with bone loss and their implants stand the risk of the implant becoming unstable in their mouth.
Bone tissue damage will continue spreading to other teeth and implant areas until medical help is provided.
Loss of bone tissue causes facial changes that affect both gum appearance and the attractiveness of your smile.
Diagnosis of Bone Loss Around Dental Implants
Doctors use these three tools to verify how dental implant spaces change in bone structure.
During patient tests, doctors use physical exams to find possible bone and gum problems.
The dentist uses X-ray pictures and 3D scans to see all bone structure elements, which helps to detect accurate bone loss measurements.
Practitioners use periodontal measuring tools to determine if bone loss exists by measuring the space between gums and teeth.
Why Does Bone Loss Occur in the Jaw?
Tooth loss or extraction stops bone stimulation underneath, which causes it to dwindle. When bones start to shrink throughout our lives, the body performs its natural remodelling process. To perform this process, the body carries out bone remodeling at both the healing and aging stages.
Losing teeth through this process decreases the bone across your entire jawbone.
The missing teeth change how your jaw and face look and how your teeth align during biting. The process of implant placement becomes more complicated once teeth are lost.
The bone degenerates quickly after tooth loss because of various conditions. These include the following:
- The jawbone risks harmful damage when you instantly remove the tooth.
- The jawbone loses its stimulation since no chewing force or tooth roots remain.
- The advanced stage of periodontal disease damages tooth tooth-supporting bone and weakens the area around your teeth.
- Bone loss proceeds at full speed unless medical measures stop its progression.
Oral surgeons employ different procedures to stop and rebuild bone loss, which follows tooth extraction procedures. Dental professionals use your excess bone or artificial replacements to rebuild areas where bone was lost.
The medical staff prescribes medicines that build bone strength while stopping bone cells from replacing themselves. Loss of a lot of bone from the jaw creates a preference for dental implants because they successfully rebuild tooth function while saving the remaining healthy bone areas.
Your jawbone remains healthier when you begin implant therapy soon after tooth loss.
How Dental Implant Treatment Works
When dental surgeons put titanium alloy material into the jawbone, they begin the osseointegration process, where the metal fuses with nearby bone.
The connected jawbone becomes ready to accept both an abutment and crown after forming complete integration with the implant.
- Stop Bone Loss in its Tracks
- Your natural teeth need the jawbone base and gum roots to stay in place.
- Your tooth roots will weaken after you lose one of them.
- The jawbone takes minerals from neighboring spaces while the gums move backward. Your tooth health will decline because your teeth will suffer damage.
A titanium dental implant serves the same purpose as a natural tooth root in the oral setting. The dental implant connects with both the jawbone and support system through its bone contact. This connection helps to preserve the existing jawbone, as the body sends instructions to maintain its status. Dental implants for oral health not only restore functionality but also promote long-term oral well-being by preventing bone loss and maintaining a healthy jaw structure.
Dental implants protect surrounding teeth by keeping their space empty of pressure.
Teeth migrate toward the vacant socket area because they no longer receive necessary support structures. As the teeth move sideways, they put excessive pressure on their chewing surface. Having a dental implant maintains the placement of your preserved teeth and protects your bone health during the restoration of your missing tooth. It’s a win-win!
You Should Receive Care Immediately
Dental implants become a suitable treatment option for everyone who has lost teeth. Having dental replacement soon after tooth loss protects your mouth and body simultaneously. Your prompt care starts protecting bone tissue during its initial damage. You must receive dental implants right after losing teeth to lower your need for bone grafting procedures.
Dental implant patients need attention because bone loss creates a serious treatment problem. Dental implants stay functional when you follow treatment schedules and take necessary dental health steps. Your dentist must first examine the bone loss problem and help decide the correct treatment.


